Discrete Automation
- Home
- Our Services
- Discrete Automation

Introduction to Discrete Automation
Discrete automation refers to automating individual tasks in manufacturing processes that involve separate, identifiable units. This includes tasks like assembly, packaging, material handling, and quality control. By leveraging technologies such as robotics, AI, and industrial automation systems, discrete automation delivers higher precision, speed, and consistency.
Applications & Cases
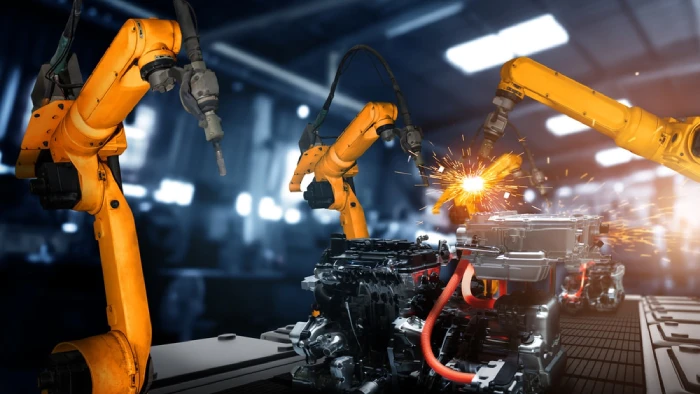
Automated Assembly
Robotic systems for precise and efficient assembly of discrete components, improving speed and accuracy while reducing manual labor.

Pick-and-Place Systems
High-speed robotic arms for sorting, picking, and placing components in production lines, ideal for electronics and automotive industries.

Quality Inspection
AI-powered vision systems ensure defect-free products by detecting errors or irregularities in size, shape, and alignment during production.

Packaging & Palletizing
Automated solutions for packing and organizing products, improving efficiency and quality while reducing handling costs.
Previous
Next
Benefits of Discrete Automation

Faster delivery times
Feature customization

Cost reduction

Improved efficiency

Increased transparency

Enhanced safety & reduced downtime
Redefine how work gets done with Robotics & AI
Harness the power of robotics, AI, and next-gen automation technologies to bring unmatched speed, accuracy, and adaptability to your manufacturing floor. Why settle for ordinary when extraordinary is just a click away? Discover how our tailored solutions can elevate your factory into a high-performing powerhouse.

